Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a commonly mystified autoimmune disorder, that causes red scaly patches of thickened skin that commonly appear on the elbows, knees, and scalp with reports of it giving a stinging and burning sensation. There are no known exact causes for psoriasis, yet it is considered a chronic condition, albeit non-contagious.There are multiple treatment options that will help you manage irritation, inflammation, and can aid in clearing the skin. The appropriate psoriasis treatment depends on the type and severity levels.
Topical psoriasis treatments range from over the counter and prescribed creams, sprays, and moisturizers. These are usually recommended for mild and sometimes moderate cases and are relatively safe. Typically, common topical treatments would be corticosteroids, retinoids, vitamin D analogues, coal tar shampoos, and salicylic acid.
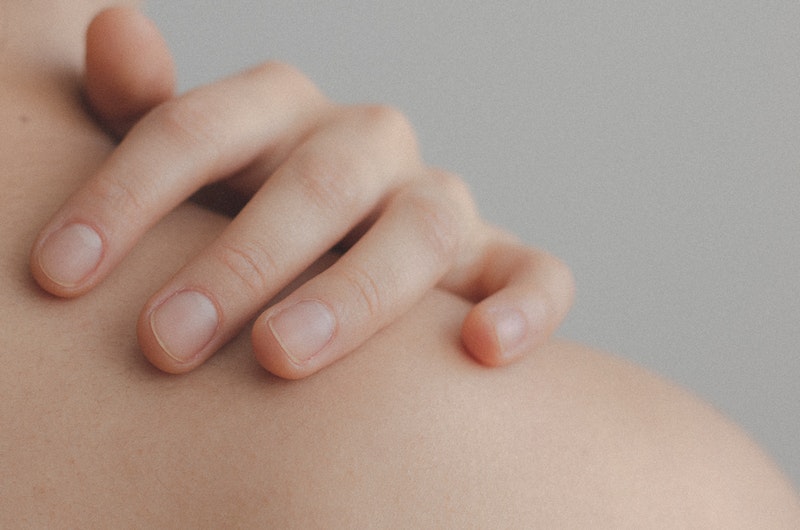

Another treatment, called phototherapy, involves exposing part of the skin to either a natural or artificial UV light source in controlled amounts. Options of phototherapy include natural sunlight which helps in reducing skin turnover, inflammation, and scaling. Broadband and narrow band UVB phototherapy is also recommended to treat widespread patches that resist topical treatments. Excimer laser therapy is also very effective in only treating the affected skin without harming healthy skin.
Other methods involve combining ultraviolet A (PUVA), with the application of a psoralen that causes the skin to be more responsive to UVA light, and crude coal tar, which causes the skin to be more responsive to UVB light. This is called the Goeckerman regimen.
If your psoriasis is severe or has rejected other types of treatment, then it may be time to look into systemic treatments, which are a group of potent oral and injected medications that doctors prescribe for usually short periods of time and monitor closely due to chances of strong side effects. Oral medications include acitretin, cyclosporine, methotrexate.
Biologics may also be an option. These are a group of mostly injected medication that alter the immune system, which have become available to treat severe psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis. They include adalimumab, abatacept, and etanercept.
While precise dietary and lifestyle studies are notably difficult to conduct, there are some indications of a relationship between psoriasis, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Low weight patients are more likely to respond to psoriasis treatment, and thus it is advised that patients maintain a healthy weight, practice extensive stress management, avoid smoking cigarettes and drinking alcohol. Anti-inflammatory diets such as fats from fish oil, olive oil, aloe vera, milk thistle, and Oregon grapes may be helpful to mild psoriasis.
Using a humidifier in your living space or office and applying moisturizers can help prevent dry skin therefore reduces the chances of plaques forming. It is recommended to avoid perfumes and soaps that have fragrance, which can irritate the skin and increase inflammation.
Psoriasis treatment can be complex but having the appropriate options for your psoriasis type and severity will maximize the effectiveness and minimize the side effects. From tweaking lifestyle choices, applying topical products, up to undergoing medically controlled UV exposure, and injection options, under a proper medical consultant, psoriasis treatment options are available.